lua源码阅读3——table
Posted on 周二 19 三月 2019 in lua源码阅读
[TOC]
Table结构体
typedef struct Table {
CommonHeader;
lu_byte flags; /* 1<<p means tagmethod(p) is not present */
lu_byte lsizenode; /* log2 of size of 'node' array 例如5标识node数组大小为32 */
unsigned int sizearray; /* size of 'array' array 数组部分的大小*/
TValue *array; /* array part */
Node *node; //哈希部分,也是一片连续内存
//例如初始有16个node, 那么lasfree=node+16
Node *lastfree; /*any free position is before this position*/
struct Table *metatable;
GCObject *gclist;
} Table;
节点的结构
typedef struct Node {
TValue i_val;
TKey i_key;
} Node;
一个节点包含一个key和value。我们主要来看看TKey:
typedef union TKey {
struct {
TValuefields;
//当前版本已经不使用链表来保存数据了,分配一片连续的内存,推测是为了加快访问速度
int next; /* for chaining (offset for next node) */
} nk; //代表着一个链表
TValue tvk; //代表着一个值
} TKey;
结构图
table的大小
/*
** Try to find a boundary in table 't'. A 'boundary' is an integer index
** such that t[i] is non-nil and t[i+1] is nil (and 0 if t[1] is nil).
*/
lua_Unsigned luaH_getn (Table *t) {
unsigned int j = t->sizearray;
if (j > 0 && ttisnil(&t->array[j - 1])) {
/* there is a boundary in the array part: (binary) search for it */
unsigned int i = 0;
//二分查找最后一个不是nil的value,i=value其下标+1,也就是个数
while (j - i > 1) {
unsigned int m = (i+j)/2;
//保证j-1始终为nil, 如果数组全为nil,最终j=1, i=0
if (ttisnil(&t->array[m - 1])) j = m;
else i = m; //如果移动过i,i-1始终不为nil
}
return i;
}
/* else must find a boundary in hash part */
else if (isdummy(t)) /* hash part is empty? */
return j; /* that is easy... */
else return unbound_search(t, j);
}
这个函数用来获取table中的数组大小,用在tabe的#运算上。我们注意到,它是通过二分查找来找的,就会导致一个有趣的现象:
#{0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, nil} == 6
#{0, 1, 2, nil, 4, 5, nil} == 6
#{0, 1, nil, 3, 4, 5, nil} == 2
因为二分法的步长把3号位的nil跳过去了。
当最后一个元素不是nil时,使用的是unbound_search来获取大小,它的本质还是一个二分查找:
static lua_Unsigned unbound_search (Table *t, lua_Unsigned j) {
lua_Unsigned i = j; /* i is zero or a present index */
j++;
//以2的幂次方为步长,找到一个为nil的下标
/* find 'i' and 'j' such that i is present and j is not */
while (!ttisnil(luaH_getint(t, j))) {
i = j;
if (j > l_castS2U(LUA_MAXINTEGER) / 2) { /* overflow? */
/* table was built with bad purposes: resort to linear search */
i = 1;
while (!ttisnil(luaH_getint(t, i))) i++;
return i - 1;
}
j *= 2;
}
//在i和i*2的区间进行二分查找
/* now do a binary search between them */
while (j - i > 1) {
lua_Unsigned m = (i+j)/2;
if (ttisnil(luaH_getint(t, m))) j = m;
else i = m;
}
return i;
}
通过这部分源代码我们可以看出来,lua认为nil为一个数组的结尾,为了不出现意外的情况,我们在建立数组时,数组里面的值最好不要有nil。
创建
创建table
Table *luaH_new (lua_State *L) {
GCObject *o = luaC_newobj(L, LUA_TTABLE, sizeof(Table));
Table *t = gco2t(o);
t->metatable = NULL;
t->flags = cast_byte(~0); //flag初始化应该为255,
t->array = NULL;
t->sizearray = 0;
setnodevector(L, t, 0);
return t;
}
创建key
/* 新建一个key,范围该key的value
** 主要用在添加非数组的值上。因为数组的key就是其下标
** inserts a new key into a hash table; first, check whether key's main
** position is free. If not, check whether colliding node is in its main
** position or not: if it is not, move colliding node to an empty place and
** put new key in its main position; otherwise (colliding node is in its main
** position), new key goes to an empty position.
*/
TValue *luaH_newkey (lua_State *L, Table *t, const TValue *key) {
Node *mp;
TValue aux;
//key不能是nil
if (ttisnil(key)) luaG_runerror(L, "table index is nil");
//检查key是否为nil, 并看能不能将float的key转成int的key
else if (ttisfloat(key)) {
lua_Integer k;
if (luaV_tointeger(key, &k, 0)) { /* does index fit in an integer? */
setivalue(&aux, k);
key = &aux; /* insert it as an integer */
}
else if (luai_numisnan(fltvalue(key)))
luaG_runerror(L, "table index is NaN");
}
//根据key的哈希值得到它应该在的节点
mp = mainposition(t, key);
//mp的value有值,或者表就是空的,需要创建新的节点
if (!ttisnil(gval(mp)) || isdummy(t)) { /* main position is taken? */
Node *othern;
Node *f = getfreepos(t); /* get a free place */
if (f == NULL) { /* cannot find a free place? */
rehash(L, t, key); /* grow table */
/* whatever called 'newkey' takes care of TM cache */
return luaH_set(L, t, key); /* insert key into grown table */
}
lua_assert(!isdummy(t));
othern = mainposition(t, gkey(mp));
//mp处的node的key得到的索引和node的下标不匹配
//说明该node不是通过hash放进去的,它应该是和othern具有相同索引的节点
//通过lastfree放进去的
if (othern != mp) { /* is colliding node out of its main position? */
/* yes; move colliding node into free position */
//找到具有相同hash的第一个节点
while (othern + gnext(othern) != mp) /* find previous */
othern += gnext(othern);
//把mp处的节点放到lastfree的位置
gnext(othern) = cast_int(f - othern); /* rechain to point to 'f' */
*f = *mp; /* copy colliding node into free pos. (mp->next also goes) */
if (gnext(mp) != 0) {
gnext(f) += cast_int(mp - f); /* correct 'next' */
gnext(mp) = 0; /* now 'mp' is free */
}
setnilvalue(gval(mp));
}
else { /* colliding node is in its own main position */
/* new node will go into free position */
if (gnext(mp) != 0)
gnext(f) = cast_int((mp + gnext(mp)) - f); /* chain new position */
else lua_assert(gnext(f) == 0);
gnext(mp) = cast_int(f - mp);
mp = f;
}
}
//在mp的节点设key, 返回value
setnodekey(L, &mp->i_key, key); //key的值
luaC_barrierback(L, t, key);
lua_assert(ttisnil(gval(mp)));
return gval(mp); //返回key对应的value
}
用图表来说明下这个过程,例如一个表的初始状态如下:
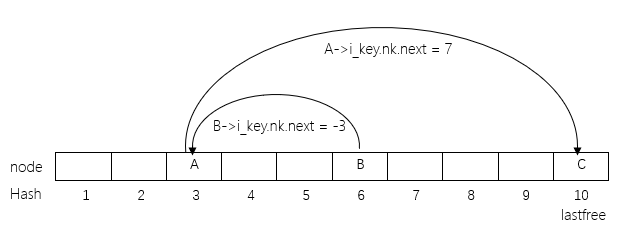
有A, B, C 三个Node, 他们的hash值都6,通过next串联起来。现在需要创建一个节点D
-
D的key的hash值指向一个空Node, 直接写进去
-
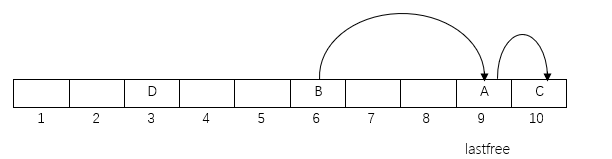
D的key的hash值指向一个非空Node,假设为A, 有两种情况
- D和A的hash值相同
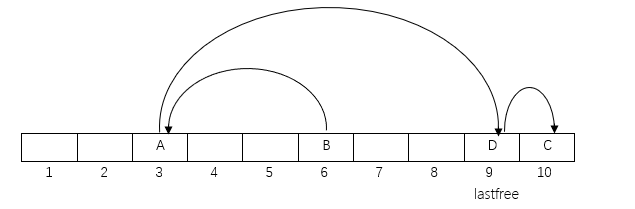
- D和A的hash值不同
扩展大小
static void rehash (lua_State *L, Table *t, const TValue *ek) {
unsigned int asize; /* optimal size for array part */
unsigned int na; /* number of keys in the array part */
//位图, 主要用来记录表中元素分布位置
//如果位于key的值不为nil,那么位图中num[ceil(log2(key))]中的值+1
//例如:key=8的值不为nil, num[3]++
unsigned int nums[MAXABITS + 1];
int i;
int totaluse;
for (i = 0; i <= MAXABITS; i++) nums[i] = 0; /* reset counts */
//将数组中的信息填入位图,na为数组中元素的个数
na = numusearray(t, nums); /* count keys in array part */
totaluse = na; /* all those keys are integer keys */
//将哈希表中的信息填入位图
totaluse += numusehash(t, nums, &na); /* count keys in hash part */
/* count extra key */
na += countint(ek, nums); //要加进去的key
totaluse++;
/* compute new size for array part */
asize = computesizes(nums, &na);
/* resize the table to new computed sizes */
luaH_resize(L, t, asize, totaluse - na);
}
简要来说:
- 对于key为数字部分,将其分布写入位图,当空间利用率大于50%的时候,扩展。
- 对于hash部分,找不到空闲节点了就需要扩展了。
查
主入口
/*
** main search function
*/
const TValue *luaH_get (Table *t, const TValue *key) {
//根据key的类型调用不同的函数来查找
switch (ttype(key)) {
case LUA_TSHRSTR: return luaH_getshortstr(t, tsvalue(key));
case LUA_TNUMINT: return luaH_getint(t, ivalue(key));
case LUA_TNIL: return luaO_nilobject;
case LUA_TNUMFLT: {
lua_Integer k;
//将float的key转成int,如果floor(key) != int(key),则进入defaut
if (luaV_tointeger(key, &k, 0)) /* index is int? */
return luaH_getint(t, k); /* use specialized version */
/* else... */
} /* FALLTHROUGH */
default: //通用查找
return getgeneric(t, key);
}
}
在这里我们看到一个比较有趣的地方,即在lua中,肯定有t[2.0] == t[2], 由于各机器上double是有精度限制的,如果10 == 10.0000000000000001, 那么t[10] == t[10.0000000000000001]。
查找key为短字符串的值
/*
** search function for short strings
*/
const TValue *luaH_getshortstr (Table *t, TString *key) {
Node *n = hashstr(t, key); //根据短字符串的哈希值找到桶
lua_assert(key->tt == LUA_TSHRSTR);
for (;;) { /* check whether 'key' is somewhere in the chain */
const TValue *k = gkey(n);
if (ttisshrstring(k) && eqshrstr(tsvalue(k), key))
return gval(n); /* that's it */
else {
int nx = gnext(n);
if (nx == 0)
return luaO_nilobject; /* not found */
n += nx;
}
}
}